- HOW TO DO
- 0 likes
- 22487 views
- 0 comments

With the advent of electronic equipment in the home, such as computers, televisions, washing machines or refrigerators, it has become increasingly important to equip apartments with surge arresters aimed at absorbing surges. As? Dumping them towards the ground.
They are mechanisms that allow you to protect all the electronic equipment in the home from overvoltages caused, for example, by storms and lightning and are characterized by two important advantages: they can be installed in any system, even existing ones and they allow you to protect yourself from serious damage , at an economical and accessible cost.
With excess voltage, the arrester absorbs the overvoltage allowing the generated current to be absorbed. The equipment to which it is connected will thus not suffer any damage.
What types of arresters are there?
Surge arresters can be of three different types:
- type 1, switching or triggering, is particularly suitable for areas affected by frequent storms, to be installed immediately under the home meter
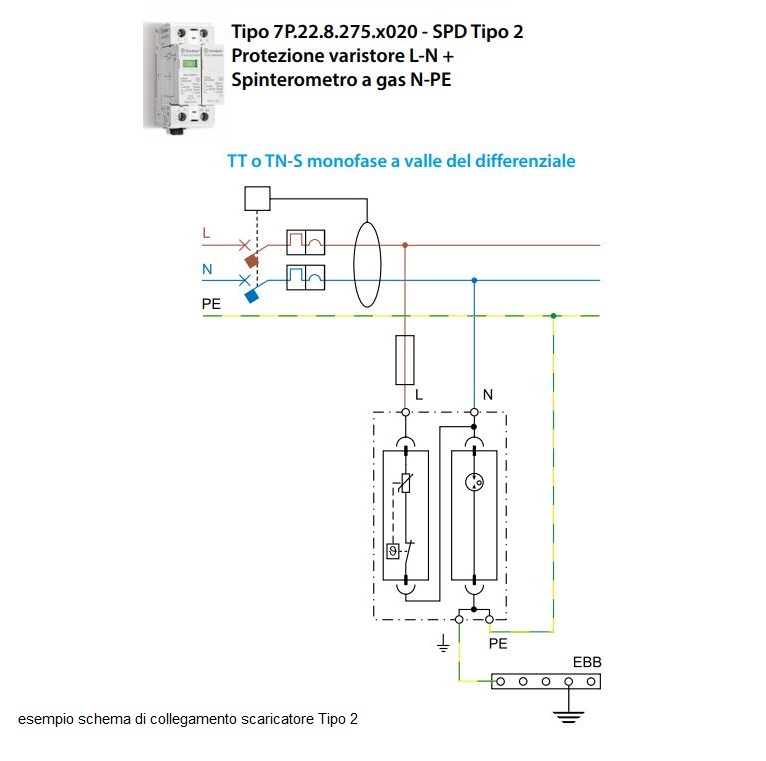
- type 2, with limitation, is indicated against overvoltages and is to be mounted directly in the home switchboard: it is composed of a varistor and a spark gap to be mounted upstream of the system and allows constant maintenance of the voltage at the terminals during absorption of overvoltage
- type 3 to be installed immediately behind the socket of the appliance you want to "safeguard".
The type 2 arrester cannot fail to absorb all the voltage, which is why it is important to also install the type 3 arrester, in order to further filter the overvoltages that may be created.
How to choose the ideal arrester?
Each surge arrester has its "nameplate data" which refers to the main characteristics of the SPD itself. It is advisable to carefully read this data in order to be able to choose the surge arrester for your type of system.
Below is a brief legend:
- [Un] rated voltage of the power system;
- [Uc] maximum continuous voltage, i.e. the value below which the arrester does not intervene;
- [Up protection voltage level, i.e. the maximum voltage value that persists at the ends of the SPD during its intervention;
- [Uoc] open-circuit voltage, i.e. the peak value of the open-circuit voltage of the combined test generator;
- [ln 8/20] nominal discharge current, i.e. the maximum value that the current can reach so that the SPD is able to discharge at least once without suffering damage;
- [limp 10/350] pulse current, i.e. the maximum value of the waveform pulse;
- protection fuse, the higher its value, the higher the quality of the varistor.
After having correctly chosen the ideal surge arrester for the protection of the system's equipment, it is advisable to install the SPD correctly. Incorrect installation could make the downloader useless.
To install it, insert the arrester into the panel and connect, via a bridge, the pure differential to the SPD, using special cables. At this point we proceed by connecting the arrester through an earth cable to the other earth cables in the apartment. If the arrester breaks, the varistor light turns from green to red, to signal the anomaly.
The surge arrester is essential for the protection of the electrical system of apartments and offices: to avoid damage and safeguard any appliance from voltage surges.




Comments (0)